Table of Contents
Verified and Tested 02/04/2015
Introduction
What we’ll be doing in this tutorial is making it so that you can no longer SSH using your root user. This is done on a fresh install of CentOS 6.5 64bit in our Cloud. We will be making a new user on the server to use as our new SSH user, and we will be setting the user up to be a sudo access user. In other words, the new user will be able to access commands as if it were the root user!
Limiting Root user in CentOS
First, we will want to SSH into our server as the root user using your preferred SSH client. Now what we will want to do is run the below command to make a new user and their home directory.
useradd newusername –d /home/newusername
You will want to change newusername to be the new user that you wish to create. After running this, you will need to create a password for the user. You can do this by running:
passwd newusername
note* Remember to always use strong passwords*
Where newusername is the new user you are creating. Now we will want to edit our sudoers file so that our new user can run commands like the root user.
visudo
In your sudoers file, you will need to locate the area that has the below information. This is where we will be adding our new user’s rights. In the picture below, it is the location under the green indicator.
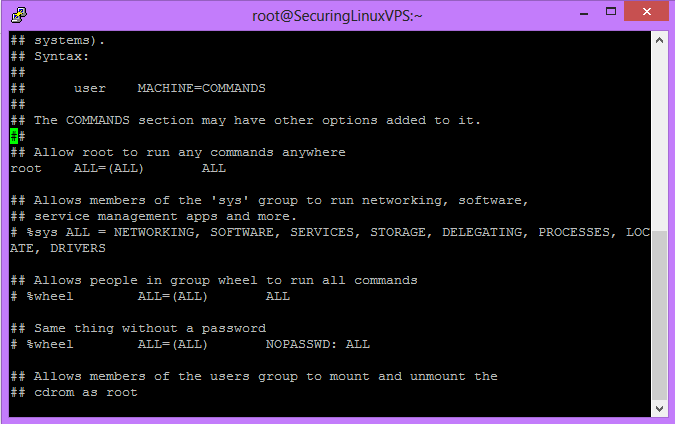
Sample Visudo Output
Right under the root entry, you will want to make the entry:
newusername ALL=(ALL) ALL
Here “newusername” is your new user.
If you don’t know how to edit in vi, you will want to (on your keyboard) hit the Insert button. Then go to the location to add the new user information and type it out. When you are done hit the ESC key on your keyboard and then do “:wq!” to save your changes.
Now the next thing to do… is test the new user! The best way to do this is to either log out or create a new SSH session using that new username and password to log in. Once you log in successfully, we can test your sudo access by going into the SSHD configuration file as the new user. This is because we still have one more change to do to prevent root log in. You can use your favorite editor for this part, we are using vi.
note*To use other commands on the server “as root” you will need to preface it with sudo.*
sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
This command will open the SSHD configuration file like you are the root user. You will want to locate the “PermiteRootLogin” option indicated by the green indictor in this picture.
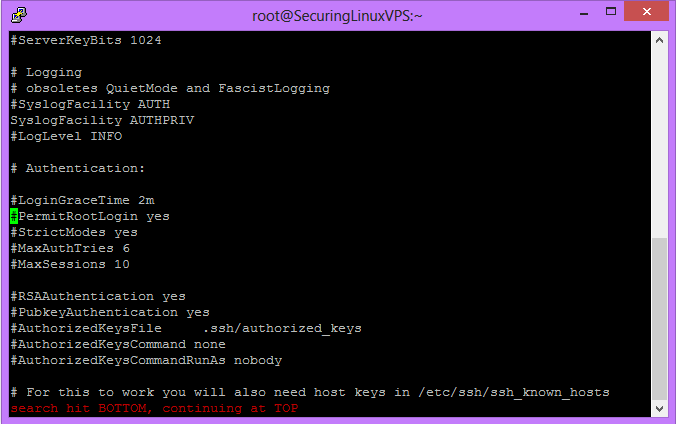
sshd_config
You will want to remove the ‘#’ and change yes to no. In the end, the line should look like
PermitRootLogin no
Once done, save and exit the file. Then run:
sudo service sshd restart
You will now be unable to SSH to your server as the root user.