Table of Contents
- What Is an IIS Server?
- How Do Web Servers Work?
- How Does a Windows Server IIS Handle Web Requests?
- How Does an IIS Web Server Work?
- How IIS Processes Requests
- IIS works with ASP.NET Core
- Versions of IIS
- Features of an IIS Server
- How to Set Up an IIS Server
- What Are the Key Advantages of Using IIS?
- Understanding Ports
- IIS vs. Apache
What Is an IIS Server?
A Microsoft IIS Server is a web application developed by Microsoft for Windows Server operating systems. Its primary function is to deliver website content over the Internet to end-users.
IIS is available as an installable server role in most editions of Microsoft Windows Server, allowing users to enable web hosting capabilities easily.
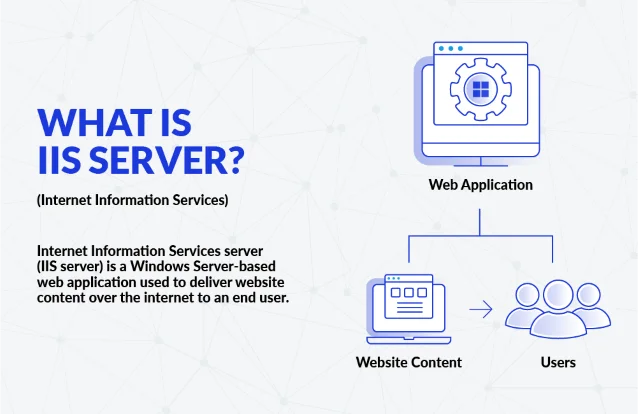
How Do Web Servers Work?
The web server front end facilitates the delivery of website content to end users over the Internet. It handles incoming requests from browsers and responds with the appropriate web pages, images, and all the resources required to display content.
How Does a Windows Server IIS Handle Web Requests?
Internet Information Services (IIS) processes web requests through a modular architecture that efficiently handles incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests from a client. When a user enters a URL and clicks on a link, the web server processes the request.
The server then opens a request-processing pipeline consisting of several stages to handle the incoming request. To see this in action, you can open your browser's developer options and refresh this page. You will see the pipeline in action.
The pipeline begins with the HTTP.sys request, which is responsible for receiving and processing incoming requests. The request then passes through various modules, including access application development features, centralized SSL certificate support, configuration file, FTP server, and transport layer security.
Each module performs specific tasks related to the request. This modular design allows administrators to customize the IIS web server behavior and optimize performance according to the website's requirements.
How Does an IIS Web Server Work?
IIS works as a multi-threaded, event-driven web server. When a request arrives at the IIS server, it is assigned to an application pool that runs in isolation. This process, known as the worker process or w3wp.exe, is responsible for handling the request and generating the response to send back to the client.
IIS supports two modes of operation: Classic mode and Integrated mode. In Classic mode, IIS primarily relies on the ISAPI (Internet Server Application Programming Interface) extensions to handle requests. However, the Integrated mode was introduced in IIS server 7.0 and offered better compatibility with ASP.NET applications and other web frameworks.
How IIS Processes Requests
IIS processes incoming requests sequentially through the request-processing pipeline. Each stage in the Internet information services pipeline performs a specific task, such as authenticating the user, handling static or dynamic content, applying security measures, and caching responses.
As the request passes through the pipeline, IIS determines which handler should be responsible for processing the request based on the requested file extension or URL. The handler generates the response, and IIS sends it back to the client.
IIS works with ASP.NET Core
IIS integrates with ASP.NET Core, Microsoft's modern and cross-platform framework for building complex web applications. Applications can be hosted on IIS using the ASP.NET Core Module, a native IIS module that forwards requests to the ASP.NET Core runtime.
This integration enables developers to utilize IIS's robust features and scalability while building dynamic and powerful browser-based applications using ASP.NET Core. It allows for easy deployment, configuration, and management of applications on Windows servers.
Versions of IIS
As IIS has evolved, each version introduced new features and enhancements. The different versions and features of IIS released alongside various versions of Windows Server are as follows:
- IIS 1.0 (1995-2002): Initial release, included with Windows NT 3.51.
- IIS 2.0 (1996-2004): Included with Windows NT 4.0.
- IIS 3.0 (1997-2005): Included with Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 2.
- IIS 4.0 (1998-2008): Included with Windows NT 4.0 Server edition.
- IIS 5.0 (2000-2010): Included with Windows 2000 Server.
- IIS 5.1 (2001-2011): Included with Windows XP Professional.
- IIS 6.0 (2003-2012): Included with Windows Server 2003.
- IIS 7.0 (2008-2020): Included with Windows Server 2008.
- IIS 7.5 (2009-2021): Included with Windows Server 2008 R2.
- IIS 8.0 (2012-2023): Included with Windows Server 2012.
- IIS 8.5 (2013-2023): Included with Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1.
- IIS 10 (2016-2027): Included with Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10.
- IIS 11 (2017-2024): Included with Windows Server 2017 and Windows 10 Anniversary Update.
- IIS 10.5 (2020-2027): Included with Windows Server 2022 and Windows 10 May 2020 Update.
Note: The numbers in the brackets represent the year of release, then the year that end-of-life support expires
Features of an IIS Server
Internet Information Services is a top choice for hosting online applications and IIS websites due to its impressive features.
Let's delve deeper into some of the key features that make IIS a preferred web server:
Native .NET and ASP.NET Support: IIS has native support for .NET and ASP.NET frameworks, making it an excellent platform for developers who prefer Microsoft technologies. This seamless integration allows developers to easily leverage these frameworks' full potential to build robust and dynamic cloud applications.
Integration with Visual Studio: One of the significant advantages of IIS is its seamless integration with Microsoft's development environment, Visual Studio. This integration streamlines web application development, offering developers a familiar and efficient development experience. With Visual Studio's tools and features working harmoniously with IIS, developers can debug, test, and deploy their internet applications seamlessly, enhancing productivity and reducing the time to market.
Application Pool: IIS utilizes the concept of application pools, which isolate digital applications from one another within the web server environment. This isolation prevents one application from affecting the performance or stability of others, enhancing security and reliability. Each application pool runs as a separate worker process, ensuring that even if one application encounters issues or crashes, it won't disrupt the functioning of other applications running on the same server.
Scalability: Scalability becomes crucial as IIS websites and applications experience increased traffic. IIS offers an excellent solution for scaling up to meet high demands by supporting the deployment of multiple servers and implementing load balancing. Administrators can distribute the incoming requests across various servers to ensure optimal performance and handle large numbers of concurrent users effectively.
Security: IIS provides a range of robust security features, such as various authentication methods, SSL encryption for secure data transmission, request filtering to prevent malicious requests, and IP restrictions to control access to the client and web server.
URL Rewrites: IIS incorporates URL rewriting capabilities, allowing administrators to manipulate URLs for improved search engine optimization (SEO) or to redirect requests. This powerful feature enables website owners to create user-friendly URLs, enhance SEO rankings, and manage URL structures effectively, ensuring a better user experience and improved visibility on search engines.
Compression: To optimize website performance and reduce bandwidth usage, IIS offers the option to compress web content before transmitting it to clients. The server can efficiently deliver content by compressing data, leading to faster load times and improved user experience, particularly for users with slower internet connections or accessing websites from mobile devices.
Centralized Management: In enterprise environments with multiple websites and web-based applications, centralized management becomes essential. IIS supports centralized management, enabling administrators to efficiently oversee and control multiple instances of IIS across various servers from a single location.
Dynamic Caching: IIS incorporates capabilities to optimize performance and reduce server workload. Frequently accessed content is cached browser side, allowing the server to quickly serve content to subsequent requests without repeatedly processing the same data. Dynamic caching significantly improves user response times, leading to a smoother and more responsive browsing experience.
Support for PHP and Other Technologies: While IIS natively supports .NET and ASP.NET, it is versatile enough to accommodate other technologies, including PHP and various scripting languages. This flexibility allows developers to choose the technology best suited to their project requirements. Whether building online applications using Microsoft's technologies or embracing popular open-source solutions like PHP, IIS provides the necessary infrastructure and compatibility to meet diverse development needs.
How to Set Up an IIS Server
Setting up an Internet Information Services (IIS) web server is crucial for hosting Internet applications effectively.
Follow these steps to configure your IIS server for optimal performance:
- Install Windows Server: Ensure you have a licensed copy of Microsoft Windows Server, a major operating system, installed on your machine. You can spin one up on the Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform.
- Install IIS: To set up IIS, navigate to "Server Manager" and add the "Web Server (IIS)" role to your server. Or Type the following into PowerShell:
- Configure IIS: Customize IIS settings based on your web application's requirements. You can set up bindings that determine how IIS responds to requests on your domain or server node. Configure domain accounts for secure access to resources.
- Application Pool: One of the essential components of IIS is the Application Pool. Create an application pool for your website, specifying the .NET version and other configurations. This segregation helps in efficiently managing resources and isolating applications for improved security.
- Deploy Web Application: Once your IIS server is ready, deploy your web application to the designated website directory. This directory can be set up on your local user folders or a remote server node.
- Test the Website: After deploying your web application, it's crucial to thoroughly test the website to ensure it is accessible and functioning as expected. Log requests using IIS to monitor the application's performance and identify potential issues.
- Web Applications and Web Developers: IIS supports hosting online platforms developed by web developers using various technologies, including WCF services. Web developers can build and deploy applications efficiently using IIS's open system platforms.
- IIS Worker Processes: IIS worker processes, also known as application pools, play a vital role in handling incoming requests. You can configure how many IIS worker processes run to optimize performance, considering hardware or reference memory limitations. Security features like Windows Authentication (Windows Auth) can be enabled to control access to your web programs effectively.
- IIS Configuration Files: The IIS configuration files hold essential settings for your web server. These files can be modified to fine-tune various aspects of your IIS setup, including worker processes and other Windows features.
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Server,Web-Common-Http,Web-Mgmt-Console
What Are the Key Advantages of Using IIS?
IIS offers several key advantages that make it a popular choice among web developers and businesses:
Native Windows Integration:
Being developed by Microsoft, IIS provides seamless integration with Windows Server operating systems. This integration allows for efficient resource utilization and easy management using familiar Windows operating system tools like Server Manager and other web management tools.
Performance and Scalability:
IIS is designed to handle high volumes of web traffic and can efficiently manage multiple client requests simultaneously through its multi-threaded architecture and worker processes. This capability makes it suitable for hosting web tools in data centers and serving large user bases.
Security Features:
IIS includes robust security features, such as Windows Authentication, to protect browser applications and sensitive data. Administrators can configure security settings and access controls through Windows Active Directory, ensuring a secure environment for web hosting.
Modular Architecture:
The modular design of IIS allows administrators to customize the web server behavior by adding or removing modules as needed. This flexibility enables fine-tuning performance and functionality based on specific application requirements.
Support for Multiple Web Technologies:
IIS supports various web technologies, including ASP.NET, PHP, and static HTML files. This broad compatibility allows developers to choose the most suitable technology for their internet applications and host them on the same server.
Application Pool Isolation:
IIS employs application pools to isolate web-based applications from one another. If one application experiences issues, it does not affect others running on the same server. This isolation improves stability and security across hosted applications.
Efficient Caching Mechanisms:
IIS includes built-in caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed content, reducing the response time for subsequent requests and improving overall server performance.
Web Deploy and Management:
IIS provides tools like Web Deploy, allowing web developers to publish web applications easily and manage website settings efficiently.
Support for .NET Framework:
IIS seamlessly supports .NET Framework applications, widely used for building robust and feature-rich web applications.
IIS GUI:
The IIS Management Console offers a user-friendly graphical interface for configuring and managing web servers and websites, making it accessible even to those with limited technical expertise.
Understanding Ports
IIS uses two primary ports to identify specific services and applications. The first port is Port 80, the default port for HTTP traffic. Whenever users access a website without specifying a port in the URL, the Windows IIS server automatically assumes that they are connecting through Port 80. This port facilitates the communication of unencrypted data between the server and the client.
The second port is Port 443, designated as the default port for HTTPS traffic. Unlike HTTP, HTTPS ensures a secure and encrypted data transmission between the server and the client, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. IIS listens on both Port 80 and Port 443 by default. Still, system administrators possess the flexibility to configure IIS to listen on different ports as required by their specific needs and configurations.
This ability to customize port settings allows for greater adaptability and ensures the smooth functioning of web services within the IIS environment.
Application Pools: What Are They and How Do They Work?
Application pools are a fundamental concept in IIS that enables isolation and enhanced performance for web applications. An application pool represents a group of web applications or websites with the same settings and runtime environment.
Each application pool operates independently, meaning that if one web application within a pool experiences issues, it does not affect other applications in different pools.
Understanding Application Pools
Application pools are a fundamental concept in IIS that enables isolation and enhanced performance for web applications. An application pool represents a group of web applications or websites with the same settings and runtime environment.
Each application pool operates independently, meaning that if one web application within a pool experiences issues, it does not affect other applications in different pools.
App Pool Users
Each application pool runs under a specific user identity known as the app pool user. This user identity determines the permissions and access rights to runtime data that the applications in the collection have on the server. By default, IIS uses the "ApplicationPoolIdentity," which provides a unique identity for each application pool.
App pool users can be customized to use different virtual user accounts based on security and access requirements. For example, administrators can configure the app pool to run under a domain user account for applications requiring access to specific network resources.
Adding an Application Pool Using IIS Manager
To add an application pool in IIS:
- Open the IIS Manager.
- Navigate to the "Application Pools" node.
- Right-click and select "Add Application Pool."
- Name the new application pool and choose the .NET version and other settings.
- Save the configuration.
App Pool Recycling
App pool recycling is where IIS periodically restarts the application pool to ensure optimal performance and memory management. Recycling helps prevent memory leaks and other issues arising from long-running applications.
Administrators can set recycling conditions based on the number of requests, specific time intervals, or memory usage thresholds. When these conditions are met, IIS will recycle the app pool, starting fresh worker processes to handle incoming requests
IIS vs. Apache
IIS and Apache are two of the most widely used web servers. Each of these web servers has its strengths and weaknesses:
Platform: IIS is native to Windows and tightly integrated with Microsoft technologies, making it an excellent choice for organizations using Windows-based infrastructure. On the other hand, Apache is open-source and runs on multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Performance: Both servers can deliver excellent performance, but performance comparisons depend on the specific use case and configuration.
Security: IIS and Apache have robust security features. While IIS has improved significantly in safety over the years, Apache's open-source nature has often been praised for its quick response to vulnerabilities and community-driven security audits.
Ease of Use: IIS may have an advantage in ease of use for Windows administrators already familiar with Microsoft products and terminology. Apache might require a steeper learning curve for those less experienced with Linux or open-source software.
Popularity: Apache historically held a larger share of the web server market, especially on Linux servers. However, IIS has gained popularity, particularly in enterprise environments, due to its seamless integration with other Microsoft products.
Are you ready to take your web hosting to the next level? Look no further than the Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform!
Harness the power of cutting-edge technology and enjoy seamless web hosting with our optimized IIS server system.
Why choose Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform for your web server needs?
Here's why:
Hassle-free Setup: Installing IIS on our cloud platform is a breeze. With just a few clicks, you can install IIS and have your web server up and running, making hosting a stress-free experience.
We offer the following flavors of Windows Server:
- Windows Server 2022 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2022 Datacenter (Desktop Experience)
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter (Desktop Experience)
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter (with Containers/Docker)
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter (Desktop Experience)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 Datacenter
High-Performance Servers: Experience lightning-fast website loading times with our robust infrastructure.
Expert Support: Our team of experts is always here to assist you. We've covered everything, from setting up your domain account to configuring Apache HTTP Server and IIS worker processes.
Seamless Integration: Whether coming from an Apache Server background or transitioning from other platforms, our cloud platform supports smooth integration with Apache Software Foundation and other open system platforms.
Scalability and Flexibility: Need more resources? No problem! Our cloud platform allows you to scale up as needed.
Enhanced Security: Your web server's security is our top priority. Benefit from advanced security features, including virtual users, server node isolation, and user mode, safeguarding your data and applications.
Don't miss this opportunity to elevate your web hosting experience. Join Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform today and unleash the true potential of your web server. Experience your web applications' seamless performance, unmatched support, and unparalleled security. Get started now and witness the difference!
Sign up today and see why the Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform is perfect for your IIS server hosting needs. Don't wait! Take the leap and experience hosting excellence with Atlantic.Net!
