Htop is a free, open-source, interactive system monitor, process viewer, and process manager designed for Linux-based operating systems. It is very similar to Task Manager in the Windows OS used to troubleshoot and kill a process that is utilizing excessive server resources. It helps the system administrator to monitor system load, CPU, memory usage, processes, and more via a command-line interface.
In this post, we will show you how to install and use Htop on Arch Linux.
Step 1 – Configure Repository
By default, the default repository is outdated in Arch Linux, so you will need to modify the default mirror list. You can do it by editing the mirrorlist configuration file:
nano /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
Remove all lines and add the following lines:
## Score: 0.7, United States Server = http://mirror.us.leaseweb.net/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 0.8, United States Server = http://lug.mtu.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch Server = http://mirror.nl.leaseweb.net/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 0.9, United Kingdom Server = http://mirror.bytemark.co.uk/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 1.5, United Kingdom Server = http://mirrors.manchester.m247.com/arch-linux/$repo/os/$arch Server = http://archlinux.dcc.fc.up.pt/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.6, United States Server = http://mirror.cs.pitt.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.7, United States Server = http://mirrors.acm.wpi.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.8, United States Server = http://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 7.1, India Server = http://mirror.cse.iitk.ac.in/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 10.1, United States Server = http://mirrors.xmission.com/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch
Save and close the file, then update all the package indexes with the following command:
pacman -Syu
Step 2 – Install Htop on Arch Linux
By default, the Htop package is included in the Arch Linux default repository. You can see the detailed information on Htop using the following command:
pacman -Si htop
You should see the following output:
Repository : extra
Name : htop
Version : 3.2.1-1
Description : Interactive process viewer
Architecture : x86_64
URL : https://htop.dev/
Licenses : GPL
Groups : None
Provides : None
Depends On : libcap libcap.so=2-64 libnl ncurses libncursesw.so=6-64
Optional Deps : lm_sensors: show cpu temperatures
lsof: show files opened by a process
strace: attach to a running process
Conflicts With : None
Replaces : None
Download Size : 144.56 KiB
Installed Size : 362.45 KiB
Packager : Christian Hesse <[email protected]>
Build Date : Fri 03 Jun 2022 06:35:51 AM UTC
Validated By : MD5 Sum SHA-256 Sum Signature
Next, install Htop using the following command:
pacman -Sy htop
Step 3 – How to Use Htop To Monitor Linux System
To use the Htop tool, open your command-line interface and run the Htop command:
htop
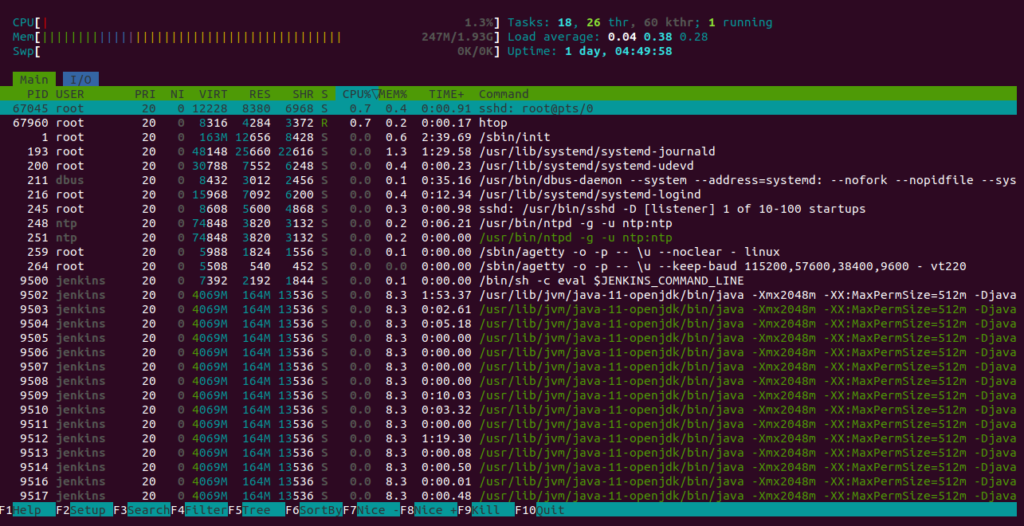
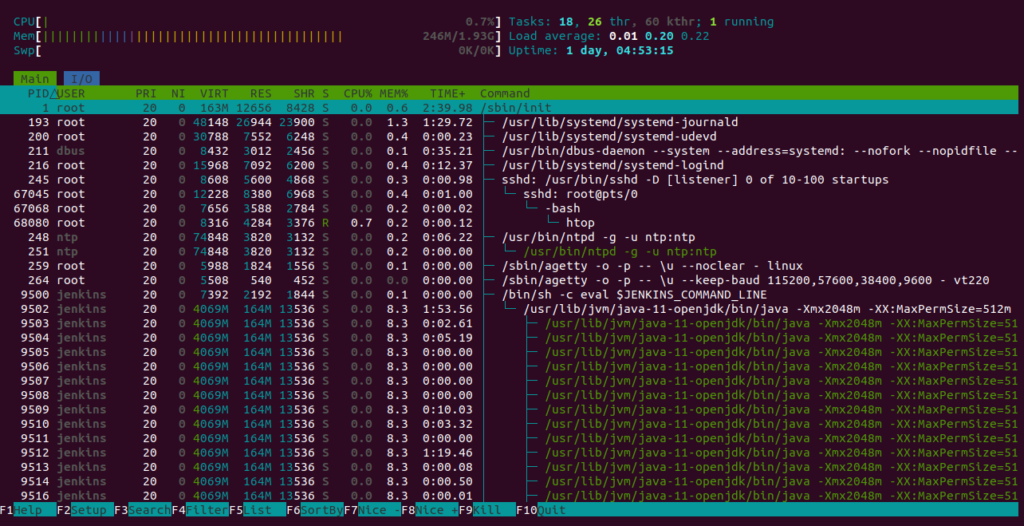
You should see all processes and system resources on the following screen:
Htop provides some common keyboard shortcuts that allow you to manage Htop.
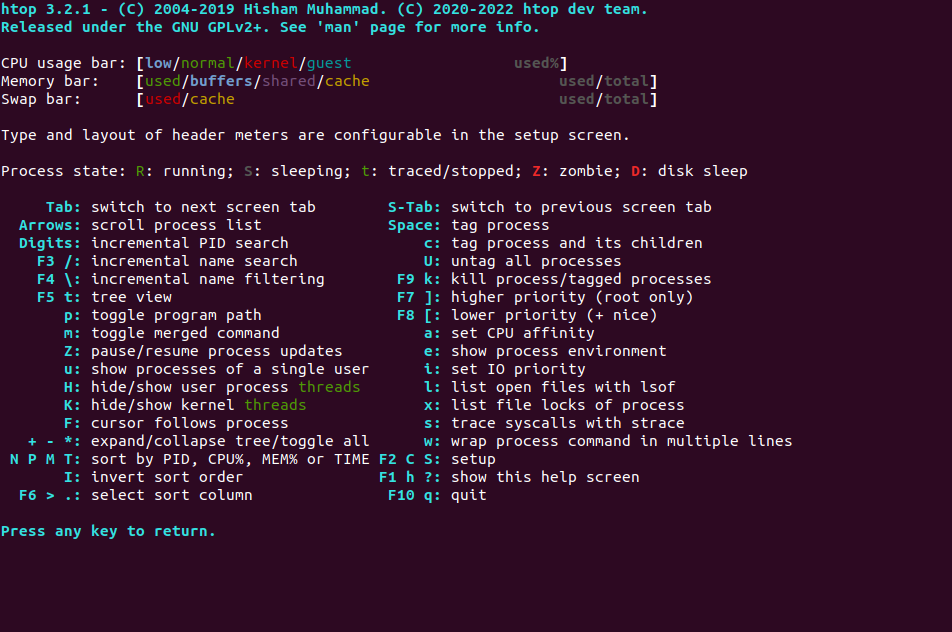
To see the help information for Htop, press the F1 key. You should see the following screen:
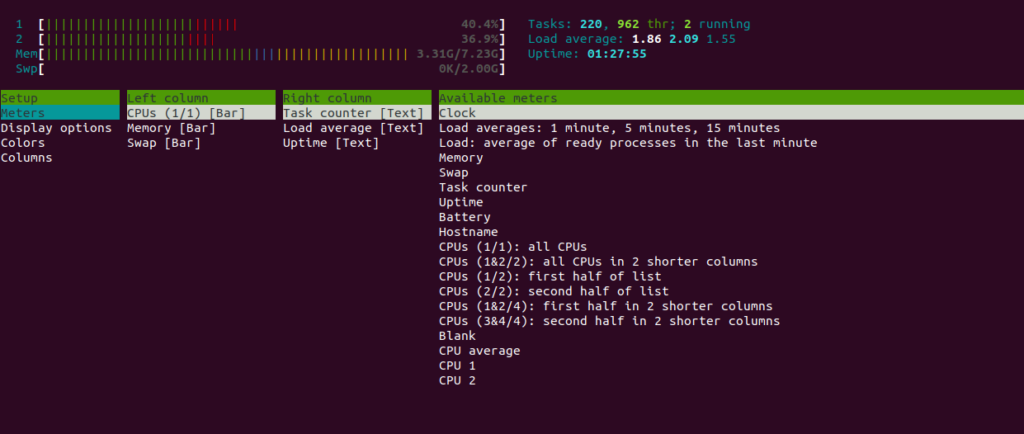
To see the setup information, press the F2 key. You should see the following screen:
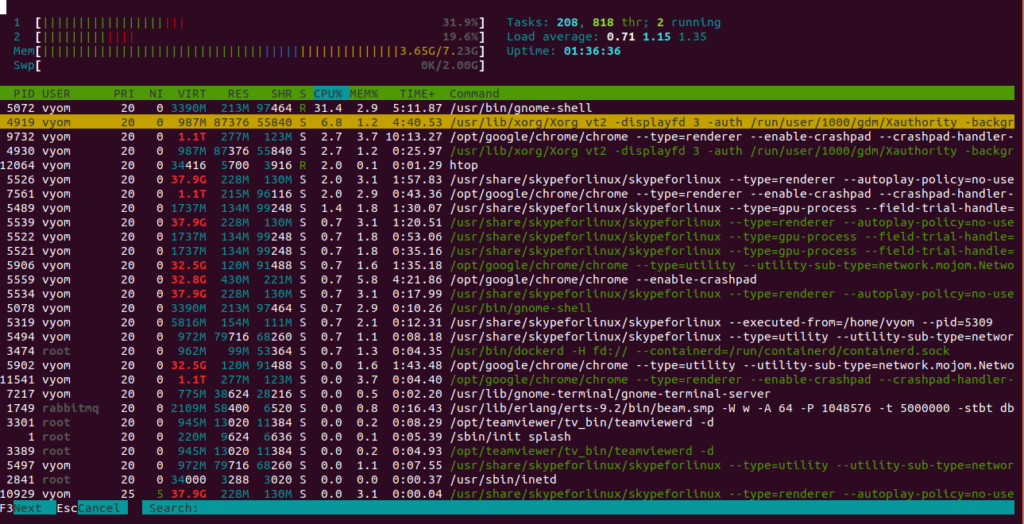
To search htop for user names and process names, press the F3 key. You should see the following screen:
To see the process tree instead of a single line per process, press the F5. You should see the following screen:
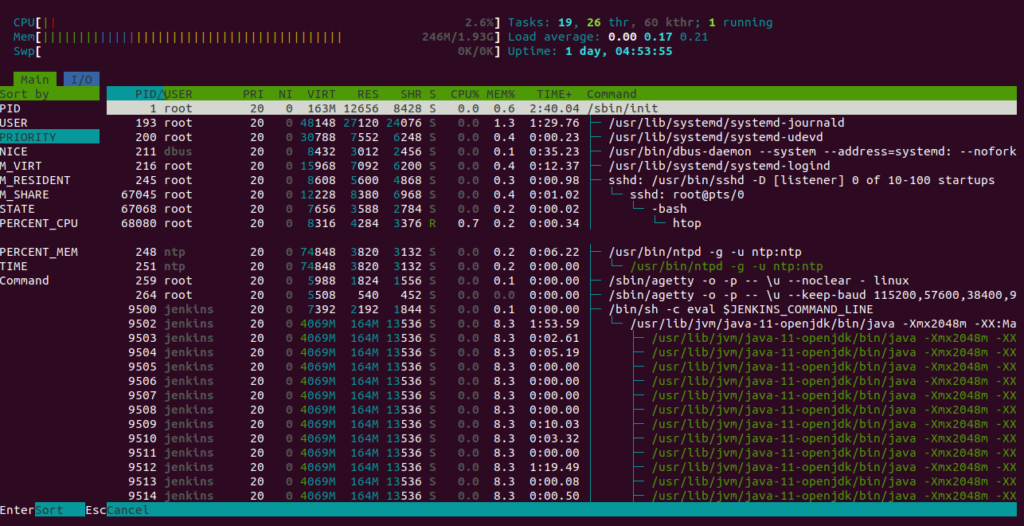
To see the individual process and sort it, press the F6. You should see the following screen:
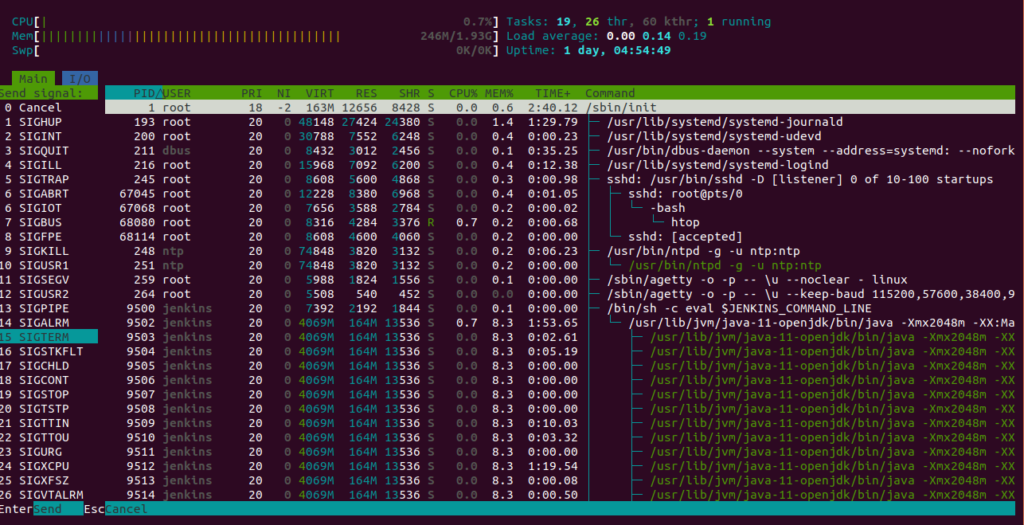
To see a list of signals that can be sent to the process, press the F9 key. You should see the following screen:
Conclusion
In this post, we explained how to install Htop on Arch Linux. We also explained how to use it to monitor the system resources. You can now install Htop on dedicated hosts from Atlantic.Net! and monitor server processes.