Introduction
PHP is a powerful, server-side scripting language designed for web development. It’s the backbone of many popular platforms such as WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, and a wide range of modern web applications. Running the latest PHP version ensures better performance, access to new features, and improved security.
By default, Debian 12 includes stable PHP packages in its official repositories, but they are not always the most recent releases. For developers who want the latest PHP version, the recommended option is to use the SURY repository, maintained by Ondřej Surý, the official Debian PHP package maintainer. This repository is widely trusted and provides up-to-date PHP versions for Debian systems.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to install PHP 8.4 on Debian 12.
Step 1 – Add the PHP PPA Repository
Debian 12 ships with PHP packages in its official repositories, but these versions may not always include the latest release. To access the newest PHP builds, you need to enable the SURY repository, which is actively maintained and trusted by the Debian community.
1. First, update your package list and install the required dependencies.
apt update -y apt install -y lsb-release apt-transport-https ca-certificates
2. Next, download and add the GPG key for the SURY repository.
wget -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/php.gpg https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg
3. Now, add the SURY repository to your system’s sources list.
echo "deb https://packages.sury.org/php/ $(lsb_release -sc) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list
4. Update the package index again so your system recognizes the new repository.
apt update -y
5. Check which PHP versions are available.
apt policy php
Output.
php:
Installed: 2:8.2+93
Candidate: 2:8.4+96+0~20250402.56+debian12~1.gbp84a5b7
Version table:
2:8.4+96+0~20250402.56+debian12~1.gbp84a5b7 500
500 https://packages.sury.org/php bookworm/main amd64 Packages
*** 2:8.2+93 500
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm/main amd64 Packages
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
This confirms that PHP 8.4 is now available from the SURY repository.
Step 2 – Install PHP 8
With the SURY repository enabled, you can now install PHP 8.4 directly on your Debian 12 system.
1. Run the following command to install PHP 8.4.
apt install -y php8.4
2. After installation, verify the PHP version.
php8.4 -v
Output.
PHP 8.4.11 (cli) (built: Aug 3 2025 08:49:56) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Built by Debian
Zend Engine v4.4.11, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.4.11, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
3. Your Debian server may have multiple PHP versions installed. To check, list the PHP directories.
ls /etc/php
You might see something like:
8.2 8.4
4. If you want PHP 8.4 to be the default version for your system, configure it using update-alternatives.
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/php php /usr/bin/php8.4 84
5. Now confirm the active PHP version.
php -v
Output.
PHP 8.4.11 (cli) (built: Aug 3 2025 08:49:56) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Built by Debian
Zend Engine v4.4.11, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.4.11, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
6. Finally, install common PHP extensions used by most applications, including MySQL, cURL, XML, and Mbstring.
apt install -y php8.4-mysql php8.4-curl php8.4-xml php8.4-mbstring
7. To confirm the installed extensions, run:
php8.4 -m
This will list all active modules available with PHP 8.4.
Step 3 – Install PHP 8 FPM
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is a modern way to run PHP applications. Instead of embedding PHP inside Apache (mod_php), PHP-FPM runs as a separate service and communicates with the web server through a socket. This separation improves performance, scalability, and security.
1. Start by installing PHP 8.4 FPM.
apt install -y php8.4-fpm
2. Next, edit the default pool configuration file.
nano /etc/php/8.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
Locate the listen directive and update it to use a Unix socket.
listen = /run/php/php8.4-fpm.sock
Set the correct ownership and permissions so Apache can access the socket.
listen.owner = www-data listen.group = www-data listen.mode = 0660
3. Now enable PHP-FPM to start automatically on boot.
systemctl enable php8.4-fpm
4. Restart the service and check its status.
systemctl restart php8.4-fpm systemctl status php8.4-fpm
Output.
● php8.4-fpm.service - The PHP 8.4 FastCGI Process Manager
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/php8.4-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-09-07 08:16:24 CAT; 4s ago
Docs: man:php-fpm8.4(8)
Process: 40083 ExecStartPost=/usr/lib/php/php-fpm-socket-helper install /run/php/php-fpm.sock /etc/php/8.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf 84 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 40080 (php-fpm8.4)
Status: "Ready to handle connections"
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4620)
Memory: 13.3M
CPU: 109ms
CGroup: /system.slice/php8.4-fpm.service
├─40080 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/8.4/fpm/php-fpm.conf)"
├─40081 "php-fpm: pool www"
└─40082 "php-fpm: pool www"
Sep 07 08:16:24 debian12 systemd[1]: Starting php8.4-fpm.service - The PHP 8.4 FastCGI Process Manager...
Sep 07 08:16:24 debian12 systemd[1]: Started php8.4-fpm.service - The PHP 8.4 FastCGI Process Manager.
This confirms that PHP-FPM is installed, configured, and running successfully.
Step 4 – Test and Use PHP 8
With PHP-FPM installed and running, you can now integrate it with the Apache web server and verify that PHP 8.4 is working correctly.
1. If Apache is not already installed on your Debian 12 system, install it with below command.
apt install -y apache2
2. Enable the proxy_fcgi and setenvif modules, which allow Apache to communicate with PHP-FPM.
a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif
3. Link Apache with the PHP 8.4 FPM configuration.
a2enconf php8.4-fpm
4. Restart Apache to apply changes.
systemctl restart apache2
5. Create a simple PHP script inside the Apache web root directory.
nano /var/www/html/test.php
Add the following code:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
6. Open your browser and navigate to:
http://SERVER-IP/test.php
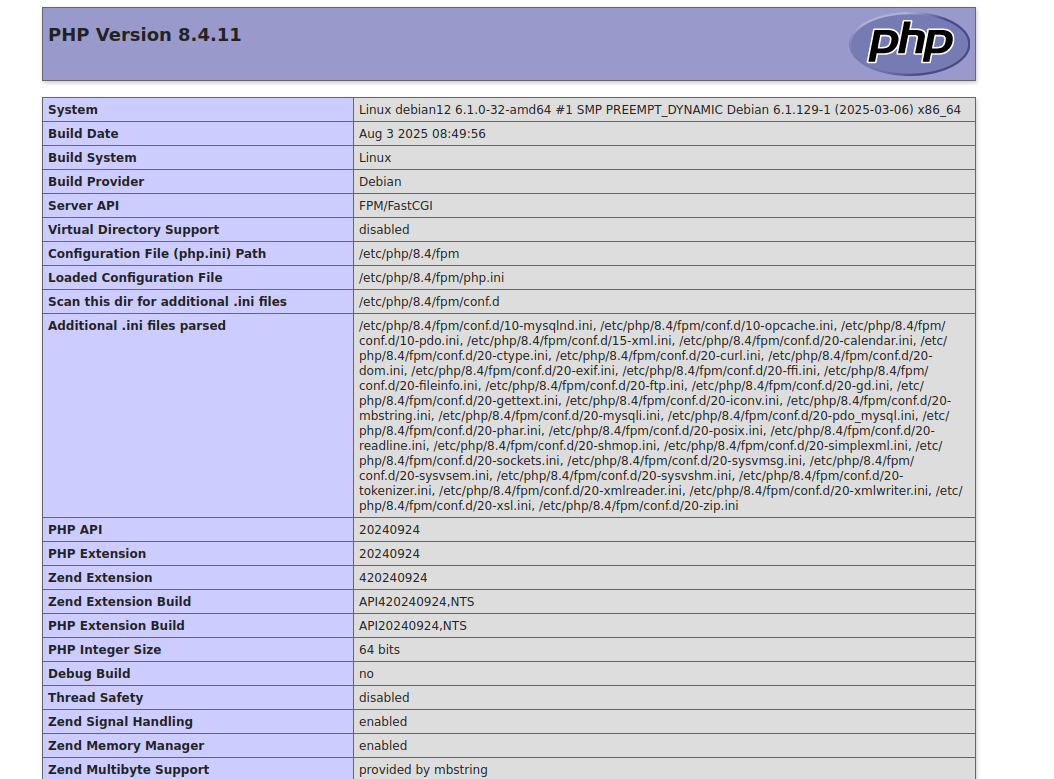
If everything is configured properly, you’ll see the PHP information page, which displays details about your PHP version, loaded modules, and server configuration.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you installed PHP 8.4 on Debian 12 using the SURY repository to access the latest release. You started by adding the repository and verifying that PHP 8.4 was available. Next, you installed PHP along with commonly used extensions and configured it as the default system version. You then set up PHP-FPM to improve performance and security by separating PHP from Apache, adjusted socket permissions, and ensured the service was running correctly. Finally, you integrated Apache with PHP-FPM and confirmed the setup by running a test PHP script in your browser.