Redmine is an open-source and cross-platform project management system. It is written in Ruby on Rails. Redmine allows you to manage multiple projects and sub-projects. It offers a web-based interface and other useful features including support for multiple languages, time tracking, role-based access control, and more. It supports various SCM integration including, SVN, CVS, Git, Mercurial, and more.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Redmine 4.2 on a Debian 10 server.
Step 1 – Install Apache and Other Packages
First, you will need to install some required dependencies on your server. You can install all of them with the following command:
apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates dirmngr gnupg2 -y
Next, install Apache, MariaDB, Passenger, and other packages with the following command:
apt-get install apache2 apache2-dev libapache2-mod-passenger mariadb-server mariadb-client build-essential ruby-dev libxslt1-dev libmariadb-dev libxml2-dev zlib1g-dev imagemagick libmagickwand-dev curl -y
After installing all the packages, you can proceed to create a database for Redmine.
Step 2 – Create a Database for Redmine
Next, you will need to create a database and user for Redmine.
First, connect to the MariaDB with the following command:
mysql
Once you are connected, create a database and user with the following command:
CREATE DATABASE redminedb CHARACTER SET utf8mb4; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON redminedb.* TO 'redmineuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Next, flush the privileges and exit from the MariaDB with the following command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Step 3 – Download and Configure Redmine
First, you will need to create a separate user for Redmine.
You can create it with the following command:
useradd -r -m -d /opt/redmine -s /usr/bin/bash redmine
Next, add the Redmine user to the www-data group with the following command:
usermod -aG www-data redmine
Next, log in to the Redmine user and download the latest version of Redmine with the following command:
su - redmine wget https://www.redmine.org/releases/redmine-4.2.1.tar.gz
Once the Redmine is downloaded, extract the downloaded file with the following command:
tar -xvzf redmine-4.2.1.tar.gz -C /opt/redmine/ --strip-components=1
Next, copy some sample configuration files with the following command:
cp /opt/redmine/config/configuration.yml{.example,}
cp /opt/redmine/public/dispatch.fcgi{.example,}
cp /opt/redmine/config/database.yml{.example,}
Next, edit the database.yml file and define your database settings:
nano /opt/redmine/config/database.yml
Change the following lines:
production: adapter: mysql2 database: redminedb host: localhost username: redmineuser password: "password"
Save and close the file, then exit from the Redmine user with the following command:
exit
Next, change the directory to /opt/redmine and install Bundler with the following command:
cd /opt/redmine gem install bundler
Next, log in to Redmine user and install the gems dependencies:
su - redmine bundle install --without development test --path vendor/bundle
Next, generate a secret token with the following command:
bundle exec rake generate_secret_token
Next, create a Rails database structure and insert default configuration data into the database with the following command:
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate RAILS_ENV=production REDMINE_LANG=en bundle exec rake redmine:load_default_data
Next, create some required files and directory with the following command:
for i in tmp tmp/pdf public/plugin_assets; do [ -d $i ] || mkdir -p $i; done
Next, set proper permission and ownership to /opt/redmine directory:
chown -R redmine:redmine files log tmp public/plugin_assets chmod -R 755 /opt/redmine
Next, exit from the Redmine user with the following command:
exit
Step 4 – Configure Apache for Redmine
Next, you will need to create an Apache virtual configuration file for Redmine. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/redmine.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName redmine.example.com
RailsEnv production
DocumentRoot /opt/redmine/public
<Directory "/opt/redmine/public">
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/redmine_error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/redmine_access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save and close the file, then enable the Redmine virtual host file and restart the Apache service with the following command:
a2ensite redmine systemctl reload apache2
Step 5 – Access Redmine
Now, open your web browser and access the Redmine web interface using the URL http://redmine.example.com. You should see the following screen:
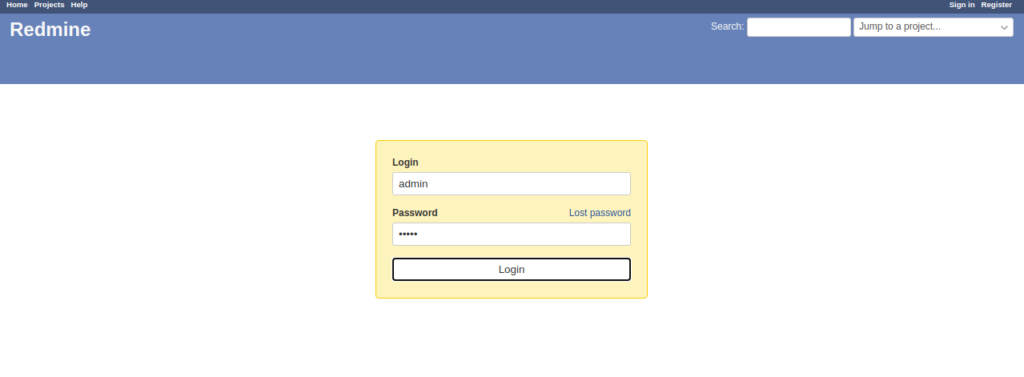
Click on the Sign In button. You should see the Redmine login screen:
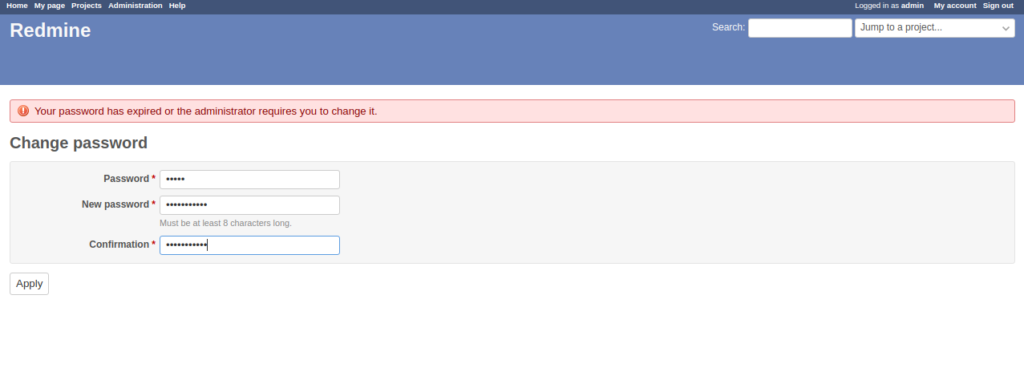
Provide the default admin username and password as admin/admin and click on the Sign in button. You will be asked to set the new password:
Provide your current password and new password, then click on the Apply button to apply the changes.
Conclusion
In this guide, you learned how to install Redmine 4.2 with Apache on Debian 10. You can now integrate Redmine with SCM tools and start managing your project. Try it out on your dedicated server hosting account from Atlantic.Net.