Cockpit is a free and open-source remote management software sponsored by Red Hat. It provides a web-based interface to manage and monitor a Linux-based server through a web browser. It runs on several operating systems, including Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, RHEL, and Arch Linux. With Cockpit, you can perform server management tasks remotely, such as manage services, create user accounts, monitor system, configure networks, inspect log, system update, manage firewall, domain management, setup OpenVPN, and many more. It also supports Kubernetes and Openshift cluster. Cockpit also provides graphs and easy-to-use forms to measure system performance and make changes to your systems.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to install Cockpit on Debian 10.
Step 1 – Install Cockpit
By default, Cockpit is available in the Debian 10 default repository. You can install it by simply running the following command:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install cockpit -y
Once Cockpit is installed, start the Cockpit service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start cockpit systemctl enable cockpit You can also verify the status of Cockpit with the following command: systemctl status cockpit
You should get the following output:
● cockpit.service - Cockpit Web Service Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.service; static; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-07-28 05:57:44 UTC; 3s ago Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8) Process: 30466 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/remotectl certificate --ensure --user=root --group=cockpit-ws --selinux-type= (code=exited, status=0/SU Main PID: 30469 (cockpit-ws) Tasks: 2 (limit: 2359) Memory: 2.2M CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.service └─30469 /usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-ws Jul 28 05:57:44 debian10 systemd[1]: Starting Cockpit Web Service... Jul 28 05:57:44 debian10 remotectl[30466]: Generating temporary certificate using: sscg --quiet --lifetime 3650 --key-strength 2048 --cert-key- Jul 28 05:57:44 debian10 remotectl[30466]: Error generating temporary dummy cert using sscg, falling back to openssl Jul 28 05:57:44 debian10 remotectl[30466]: Generating temporary certificate using: openssl req -x509 -days 36500 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ Jul 28 05:57:44 debian10 systemd[1]: Started Cockpit Web Service. Jul 28 05:57:44 debian10 cockpit-ws[30469]: Using certificate: /etc/cockpit/ws-certs.d/0-self-signed.cert
Step 2 – Access Cockpit Web Interface
At this point, Cockpit is installed and listening on port 9090. You can verify the listening port with the following command:
apt install net-tools -y netstat -tunelp | grep 9090 You should see the following output: tcp6 0 0 :::9090 :::* LISTEN 0 192987 1/init
Now, open your web browser and access the Cockpit web UI using the URL https://your-server-ip:9090. You will be redirected to the Cockpit web interface as shown below:
Provide your system root username and password, and click on the Log in button. You should see the Cockpit dashboard in the following screen:
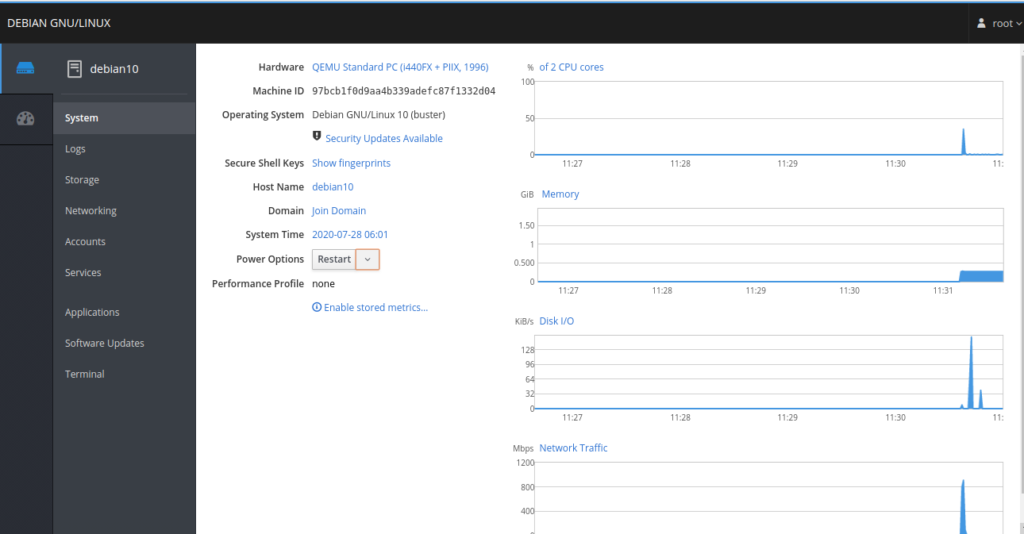
In the above screen, you should see the summary of your system information and performance graphs for CPU, Memory, Disk I/O, and network traffic.
Step 3 – How to Use Cockpit
In this section, we will show you how to use Cockpit web interface.
In the left pane, you should see a lot of useful options.
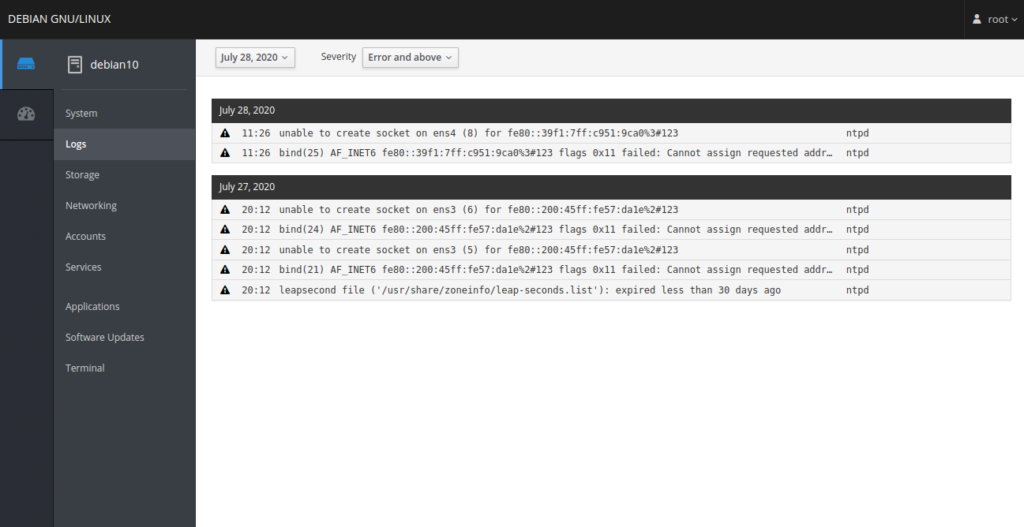
In the left pane, click on the Logs menu. You should see the logs page which allows for logs inspection.
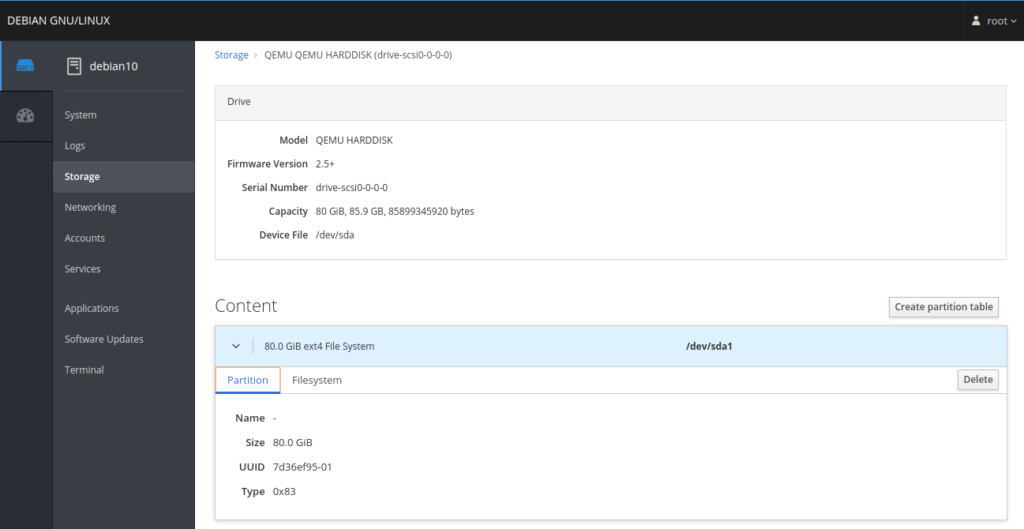
The Storage menu provides a summary of the system disk, partition, and file system as shown below:
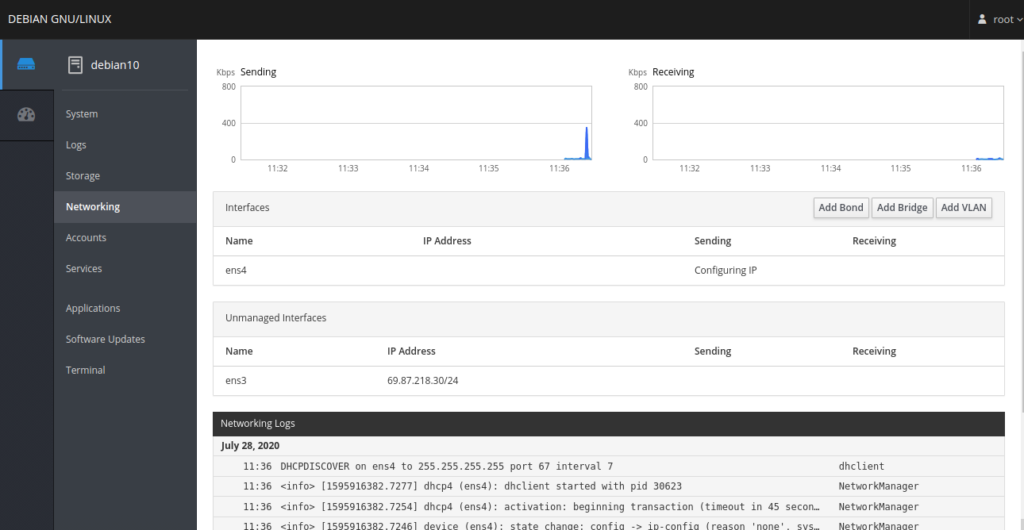
The Networking menu provides network interface, IP address, and traffic information. You can also add Bond, Bridge, and VLAN using this menu.
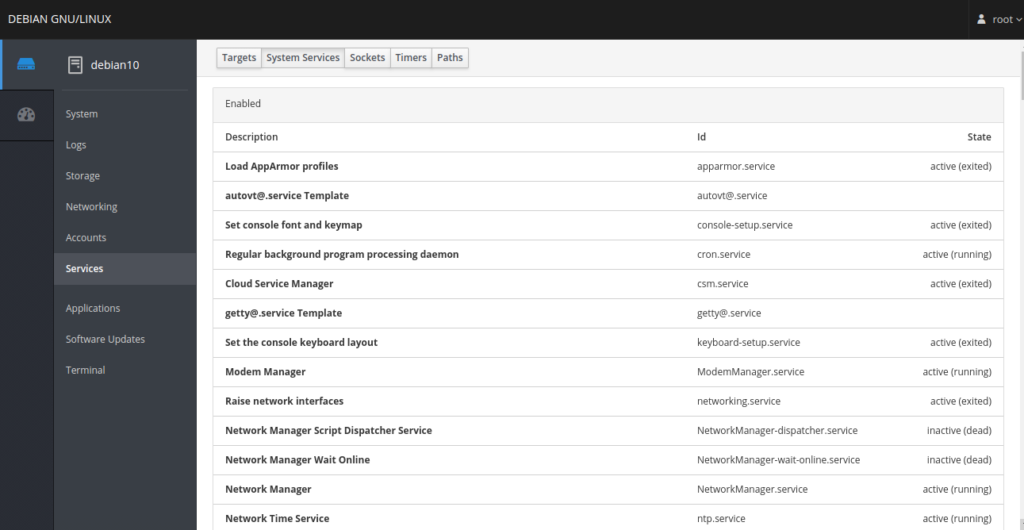
With the Services menu, you can see Targets, System Services, Sockets, Timers, and Paths pages. You can also manage system services using this menu.
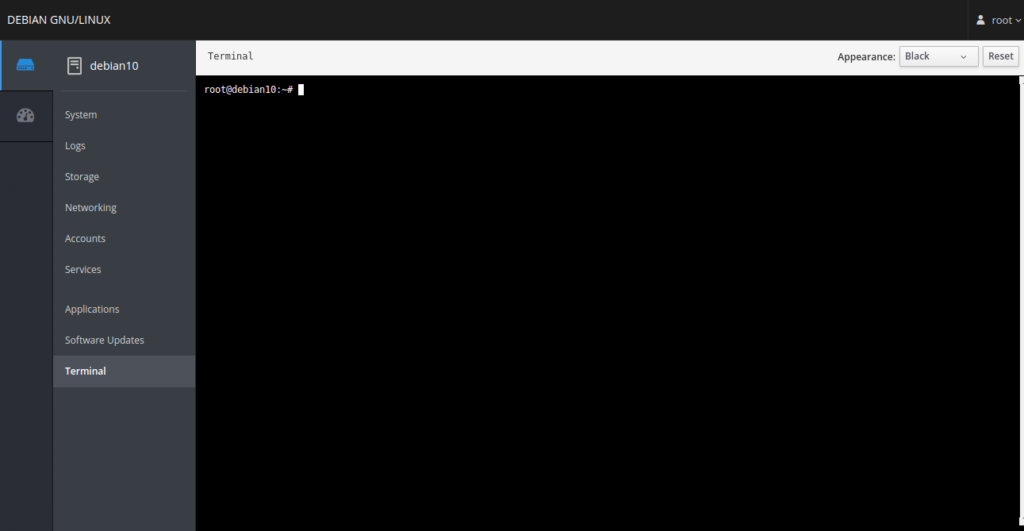
The Terminal menu provides a command-line interface to execute commands in your system.
Conclusion
In this guide, you learned how to install and use Cockpit on Debian 10. This tool is very useful for Linux beginners who don’t know the command-line and helps you to control a Linux server through a web interface. Get started with Cockpit on your Linux server on VPS Hosting from Atlantic.Net!
